Example-Using a Raw Device as the NCA Log File
The logd_path_name string in ncalogd.conf can define a raw device as the place to store the NCA log file. The advantage to using a raw device is that the service can run faster because the overhead in accessing a raw device is less.
The NCA service tests any raw device that is listed in the file to ensure that no file system is in place. This test ensures that no active file systems are accidentally written over.
To prevent this test from finding a good file system, run the following command to destroy part of the file system on any disk partition that was originally configured as a file system. In this example, /dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7 is the raw device that has an old file system on it.
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7 bs=1024 count=1 |
After running dd, you can then add the raw device to the ncalogd.conf file
# cat /etc/nca/ncalogd.conf # # NCA Logging Configuration File # status=enabled logd_path_name="/dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7" logd_file_size=1000000 |
Example-Using Multiple Files for NCA Logging
The logd_path_name string in ncalogd.conf can define multiple targets as the place to store the NCA log file. The second file is used when the first file is full. The following example shows how to select to write to the /var/nca/log file first and then use a raw partition.
# cat /etc/nca/ncalogd.conf # # NCA Logging Configuration File # status=enabled logd_path_name="/var/nca/log /dev/rdsk/c0t0d0s7" logd_file_size=1000000 |
 How to Disable Caching of Web Pages
How to Disable Caching of Web Pages
Become superuser.
Disable the ncakmod kernel module.
Change the status entry in /etc/nca/ncakmod.conf to disabled.
# cat /etc/nca/ncakmod.conf # NCA Kernel Module Configuration File # status=disabled httpd_door_path=/var/run/nca_httpd_1.door nca_active=disabled
Disable NCA logging.
Change the status entry in /etc/nca/ncalogd.conf to disabled.
# cat /etc/nca/ncalogd.conf # # NCA Logging Configuration File # status=disabled logd_path_name="/var/nca/log" logd_file_size=1000000
Reboot the server.
 How to Enable or Disable NCA Logging
How to Enable or Disable NCA Logging
NCA logging can be turned on or off as needed after NCA has been enabled. See "How to Enable Caching of Web Pages" for more information.
Become superuser.
Change NCA logging.
To permanently disable logging, you need to change the status in /etc/nca/ncalogd.conf to disabled and reboot the system. See the ncalogd.conf(4) man page for more information.
 How to Load the NCA Socket Utility Library
How to Load the NCA Socket Utility Library
Follow this process only if your web server does not provide native support of the AF_NCA socket.
Add a line to the web server startup script that causes the library to be preloaded. The line should resemble the following:
LD_PRELOAD=/usr/lib/ncad_addr.so /usr/bin/httpd |
Caching Web Pages (Reference)
The following sections cover the files and components that are needed to use NCA. Also, specifics about how NCA interacts with the web server are included.
NCA Files
You need several files to support the NCA feature. Many of these files are ASCII, but some of them are binary. The following table lists all of the files.
Table 2-1 NCA Files
File Name | Function |
|---|---|
File that lists all physical interfaces that are configured on the server. | |
File that lists all host names that are associated with the server. Entries in this file must match entries in /etc/hostname.* files for NCA to function. | |
Script that starts the NCA server. This script is run when a server is booted. | |
Script that starts NCA logging. This script is run when a server is booted. | |
File that lists the interfaces on which NCA is run. See the nca.if(4) man page for more information. | |
File that lists configuration parameters for NCA. See the ncakmod.conf(4) man page for more information. | |
File that lists configuration parameters for NCA logging. See the ncalogd.conf(4) man page for more information. | |
Command that is used to convert data in the log file to the common log format. See the ncab2clf(1) man page for more information. | |
Command that is used to configure NCA to run on multiple interfaces during boot. See the ncaconfd(1M) man page for more information. | |
Library that uses AF_NCA sockets instead of AF_INET sockets. This library must be used on web servers that use AF_INET sockets. See the ncad_addr(4) man page for more information. | |
File that holds the log file data. The file is in binary format, so do not edit it. |
NCA Architecture
The NCA feature includes the following components.
Kernel module, ncakmod
Web server, httpd
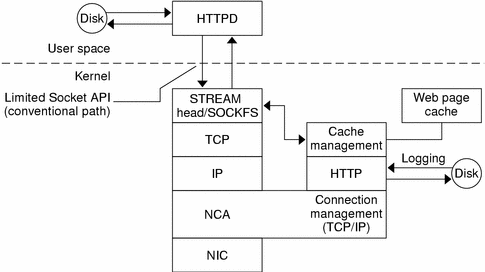
The kernel module ncakmod maintains the cache of web pages in system memory. The module communicates with a web server, httpd, through a sockets interface (family type PF_NCA).
The kernel module also provides a logging facility that logs all HTTP cache hits. NCA logging writes HTTP data to the disk in binary format. NCA provides a conversion utility for converting binary log files to common log format (CLF).
The following figure shows the flow of data for the conventional path and the path that is used when NCA is enabled.
Figure 2-1 Data Flow with the NCA Service