How to Create a Role From the Command Line
How to Create a Role From the Command Line
Become superuser or assume a role that is capable of creating other roles.
Select a method for creating a role:
For roles in the local scope, use the roleadd command to specify a new local role and its attributes.
Alternatively, for roles in the local scope, edit the user_attr file to add a user with type=role.
This method is recommended for emergencies only, as it is easy to make mistakes while you are typing.
For roles in a name service, use the smrole command to specify the new role and its attributes.
This command requires authentication by superuser or a role that is capable of creating other roles. You can apply the smrole to all name services. This command runs as a client of the Solaris Management Console server.
Start and stop the name service cache daemon.
New roles do not take effect until the name service cache daemon is restarted. As root, type as follows:
# /etc/init.d/nscd stop # /etc/init.d/nscd start
Example 18-1 Creating a Custom Operator Role by Using the smrole Command
The following sequence demonstrates how a role is created with the smrole command. In this example, a new version of the Operator role is created that has assigned to it the standard Operator rights profile and the Media Restore rights profile.
% su primaryadmin # /usr/sadm/bin/smrole add -H myHost -- -c "Custom Operator" -n oper2 -a johnDoe \ -d /export/home/oper2 -F "Backup/Restore Operator" -p "Operator" -p "Media Restore" Authenticating as user: primaryadmin Type /? for help, pressing <enter> accepts the default denoted by [ ] Please enter a string value for: password :: <type primaryadmin password> Loading Tool: com.sun.admin.usermgr.cli.role.UserMgrRoleCli from myHost Login to myHost as user primaryadmin was successful. Download of com.sun.admin.usermgr.cli.role.UserMgrRoleCli from myHost was successful. Type /? for help, pressing <enter> accepts the default denoted by [ ] Please enter a string value for: password ::<type oper2 password> # /etc/init.d/nscd stop # /etc/init.d/nscd start |
To view the newly created role (and any other roles), use smrole with the list subcommand, as follows:
# /usr/sadm/bin/smrole list -- Authenticating as user: primaryadmin Type /? for help, pressing <enter> accepts the default denoted by [ ] Please enter a string value for: password :: <type primaryadmin password> Loading Tool: com.sun.admin.usermgr.cli.role.UserMgrRoleCli from myHost Login to myHost as user primaryadmin was successful. Download of com.sun.admin.usermgr.cli.role.UserMgrRoleCli from myHost was successful. root 0 Super-User primaryadmin 100 Most powerful role sysadmin 101 Performs non-security admin tasks oper2 102 Backup/Restore Operator |
Changing Role Properties
To change a role, you must either assume a role that has the Primary Administrator rights profile assigned to it, or run the User Tool Collection as root user if roles have not yet been set up.
 How to Change a Role by Using the Administrative Roles Tool
How to Change a Role by Using the Administrative Roles Tool
Start the Administrative Roles tool.
To run the Administrative Roles tool, you need to start the Solaris Management Console, as described in "How to Assume a Role in the Console Tools". Then, open the User Tool Collection, and click the Administrative Roles icon.
After the Administrative Roles tool starts, the icons for the existing roles are displayed in the view pane.
Click the role to be changed and select the appropriate item from the Action menu, as follows:
To change users who are assigned to a role, select Assign Administrative Role.
The Assign Administrative Role dialog box is displayed. The Assign Administrative Role dialog box is a modified version of the Role Properties dialog box and has a Users tab only. Use the Add field to assign a user in the current scope to this role. Use the Delete field to remove a user's role assignment. Click OK to save.
To change rights that are assigned to a role, select Assign Rights to Role.
The Assign Rights to Role dialog box is displayed. The Assign Rights to Role dialog box is a modified version of the Role Properties dialog box and has a Rights tab only. Use the Available Rights and Granted Rights columns to add or remove rights profiles for the selected role. Click OK to save.
To change any of the role's properties, select Properties (or simply double-click the role icon).
The Role Properties dialog box is displayed, which provides access to all role properties (see the following figure and table). Use the tabs to navigate to any information to be changed, make your changes, and click OK to save.
Figure 18-4 Role Properties Dialog Box
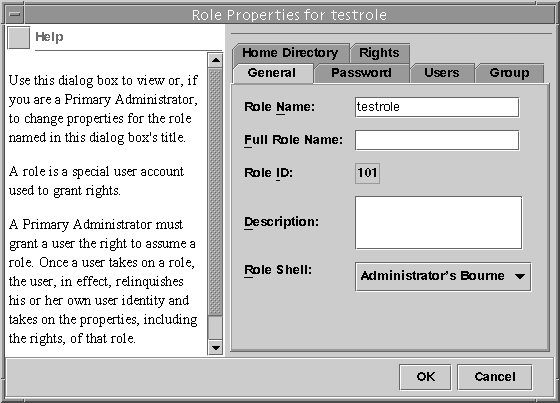
Table 18-2 Role Properties Summary
Tab Description
General
Specifies the role identification information and the default login shell.
Password
Specifies the role password.
Users
Specifies the users who are assigned to the role.
Group
Sets the role's primary groups and secondary groups for the purpose of accessing and creating files and directories.
Home Directory
Specifies the role's home directory, home directory server, automounting, and directory access.
Rights
Allows rights profiles to be assigned to the role. The precedence of the assigned rights profiles can be changed here.
 How to Change a Role From the Command Line
How to Change a Role From the Command Line
Become superuser or assume a role that is capable of changing other roles.
Use the command that is appropriate for the task:
Use the rolemod command to modify the attributes of a role that are defined locally.
Use the roledel command to delete a role that is defined locally.
Edit the user_attr file to change the authorizations or rights profiles that are assigned to a local role.
This method is recommended for emergencies only, as it is easy to make a mistake while you are typing.
Use the smrole command to modify the attributes of a role in a name service.
This command requires authentication as superuser or as a role that is capable of changing other roles. The smrole command runs as a client of the Solaris Management Console server.