GSS-API Reference
This appendix includes the following sections:
"GSS-API Functions" provides a table of GSS-API functions.
"GSS-API Status Codes" discusses status codes returned by GSS-API functions, and provides a list of those status codes.
"GSS-API Data Types and Values" discusses the various data types used by the GSS-API.
Additional GSS-API definitions can be found in the file gssapi.h.
GSS-API Functions
The following table lists the functions of the GSS-API. For more information on each function, see its man page. See also "Functions From Previous Versions of the GSS-API".
Table B-1 GSS-API Functions
Function | Description |
|---|---|
gss_acquire_cred() | Assume a global identity; obtain a GSS-API credential handle for pre-existing credentials |
gss_add_cred() | Construct credentials incrementally |
gss_inquire_cred() | Obtain information about a credential |
gss_inquire_cred_by_mech() | Obtain per-mechanism information about a credential |
gss_release_cred() | Discard a credential handle |
gss_init_sec_context() | Initiate a security context with a peer application |
gss_accept_sec_context() | Accept a security context initiated by a peer application |
gss_delete_sec_context() | Discard a security context |
gss_process_context_token() | Process a token on a security context from a peer application |
gss_context_time() | Determine for how long a context will remain valid |
gss_inquire_context() | Obtain information about a security context |
gss_wrap_size_limit() | Determine token-size limit for gss_wrap() on a context |
gss_export_sec_context() | Transfer a security context to another process |
gss_import_sec_context() | Import a transferred context |
gss_get_mic() | Calculate a cryptographic message integrity code (MIC) for a message; integrity service |
gss_verify_mic() | Check a MIC against a message; verify integrity of a received message |
gss_wrap() | Attach a MIC to a message, and optionally encrypt the message content |
gss_unwrap() | Verify a message with attached MIC, and decrypt message content if necessary |
gss_import_name() | Convert a contiguous string name to internal-form |
gss_display_name() | Convert internal-form name to text |
gss_compare_name() | Compare two internal-form names |
gss_release_name() | Discard an internal-form name |
gss_inquire_names_for_mech() | List the name types supported by the specified mechanism |
gss_inquire_mechs_for_name() | List mechanisms that support the specified name type |
gss_canonicalize_name() | Convert an internal name to an MN |
gss_export_name() | Convert an MN to export form |
gss_duplicate_name() | Create a copy of an internal name |
gss_add_oid_set_member() | Add an object identifier to a set |
gss_display_status() | Convert a GSS-API status code to text |
gss_indicate_mechs() | Determine available underlying authentication mechanisms |
gss_release_buffer() | Discard a buffer |
gss_release_oid_set() | Discard a set of object identifiers |
gss_create_empty_oid_set() | Create a set containing no object identifiers |
gss_test_oid_set_member() | Determine whether an object identifier is a member of a set |
Functions From Previous Versions of the GSS-API
This section explains functions that were included in previous versions of the GSS-API.
Functions for Manipulating OIDs
The following functions are supported by the Sun implementation of the GSS-API for convenience and for backward compatibility with programs written for older versions of the GSS-API. However, they should not be relied upon, as they might not be supported by other implementations of the GSS-API.
Although these functions make it possible to convert a mechanism's name from a string to an OID, programmers should use the default GSS-API mechanism, instead of specifying one, if at all possible.
Renamed Functions
The following functions have been supplanted by newer functions. In each case, the new function is the functional equivalent of the old one. Although the old functions are supported, developers should replace them with the newer functions whenever possible.
GSS-API Status Codes
Major status codes are encoded in the OM_uint32 as shown in Figure B-1.
Figure B-1 Major-Status Encoding
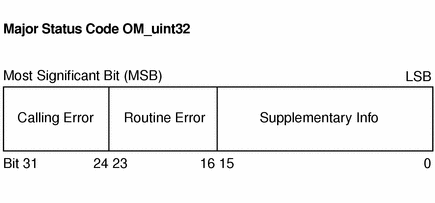
If a GSS-API routine returns a GSS status code whose upper 16 bits contain a non-zero value, the call has failed. If the calling error field is non-zero, the invoking application's call of the routine was erroneous. Calling errors are listed in Table B-2. If the routine error field is non-zero, the routine failed because of a routine-specific error, as listed below in Table B-3. Whether or not the upper 16 bits indicate a failure or a success, the routine might indicate additional information by setting bits in the supplementary information field of the status code. The meaning of individual bits is listed in Table B-4.
GSS-API Major Status Code Values
The following tables lists calling errors returned by the GSS-API; that is, errors that are specific to a particular language-binding (C, in this case).
Table B-2 Calling Errors
Error | Value in Field | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_READ | 1 | A required input parameter could not be read |
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_WRITE | 2 | A required output parameter could not be written |
GSS_S_CALL_BAD_STRUCTURE | 3 | A parameter was malformed |
The following table lists the routine errors (that is, generic errors returned by GSS-API functions).
Table B-3 Routine Errors
Error | Value in Field | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
GSS_S_BAD_MECH | 1 | An unsupported mechanism was requested |
GSS_S_BAD_NAME | 2 | An invalid name was supplied |
GSS_S_BAD_NAMETYPE | 3 | A supplied name was of an unsupported type |
GSS_S_BAD_BINDINGS | 4 | Incorrect channel bindings were supplied |
GSS_S_BAD_STATUS | 5 | An invalid status code was supplied |
GSS_S_BAD_MIC, GSS_S_BAD_SIG | 6 | A token had an invalid MIC |
GSS_S_NO_CRED | 7 | No credentials were supplied, or the credentials were unavailable or inaccessible |
GSS_S_NO_CONTEXT | 8 | No context has been established |
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_TOKEN | 9 | A token was invalid |
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_CREDENTIAL | 10 | A credential was invalid |
GSS_S_CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED | 11 | The referenced credentials have expired |
GSS_S_CONTEXT_EXPIRED | 12 | The context has expired |
GSS_S_FAILURE | 13 | Miscellaneous failure. The underlying mechanism detected an error for which no specific GSS-API status code is defined. The mechanism-specific status code (minor-status code) provides more details about the error. |
GSS_S_BAD_QOP | 14 | The quality-of-protection requested could not be provided |
GSS_S_UNAUTHORIZED | 15 | The operation is forbidden by local security policy |
GSS_S_UNAVAILABLE | 16 | The operation or option is unavailable |
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_ELEMENT | 17 | The requested credential element already exists |
GSS_S_NAME_NOT_MN | 18 | The provided name was not a Mechanism Name (MN) |