Remote Shared Memory API for Solaris Clusters
Solaris Cluster OS™ systems can be configured with a memory-based interconnect (for example, Dolphin-SCI) and layered system software components. These components implement a mechanism for user-level inter-node messaging based on direct access to memory residing on remote nodes. This mechanism is referred to as Remote Shared Memory (RSM). This chapter defines the RSM Application Programming Interface (RSMAPI).
"API Framework" describes the RSM API framework.
"API Library Functions" covers RSM API library functions.
"RSMAPI Usage Example" shows an example of use.
Overview of the Shared Memory Model
In the shared memory model, an application process creates an RSM export segment from the process's local address space. One or more remote application processes create an RSM import segment with a virtual connection between export and import segments across the interconnect. All processes make memory references for the shared segment with addresses local to their specific address space.
An application process creates an RSM export segment by allocating locally addressable memory to the export segment using one of the standard Solaris interfaces (for example, System V Shared Memory, mmap(2), or valloc(3C)). The process then calls on the RSMAPI for the creation of a segment, which provides a reference handle for the allocated memory. The RSM segment is published (made remotely accessible) through one or more interconnect controllers, along with a list of access privileges for those nodes that are permitted to import the segment.
A segment ID is assigned to the exported segment. This segment ID, along with the cluster node ID of the creating process, allows an importing process to uniquely specify an export segment. Successfully creating an export segment returns a segment handle to the process for use in subsequent segment operations.
An application process obtains access to a published segment by using the RSMAPI to create an import segment and form a virtual connection across the interconnect. Successfully creating this import segment returns an RSM import segment handle to the application process for use in subsequent segment import operations. After establishing the virtual connection, the application may request RSMAPI to provide a memory map for local access, if supported by the interconnect. If memory mapping is not supported, the application can use memory access primitives provided by RSMAPI.
The RSMAPI provides a mechanism (called a barrier) to support remote access error detection and resolve write-order memory model issues.
RSMAPI provides a notification mechanism to synchronize local and remote accesses. An export process can call a function to block pending a data write by an import process. When the import process finishes writing, it unblocks the export process by calling a signal function. Once unblocked, the export process processes the data.
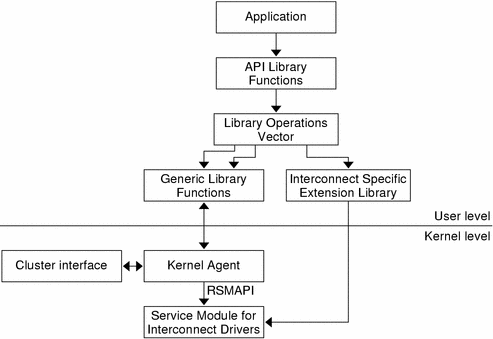
API Framework
The RSM application support components are delivered in software packages as follows:
-
A shared library (/usr/lib/librsm.so) that exports the RSMAPI functions.
A Kernel Agent (KA) pseudo device driver (/usr/kernel/drv/rsm) that interfaces with the memory interconnect driver through the RSMAPI interface on behalf of the user library
A cluster interface module for obtaining interconnect topology.
-
Interconnect driver service module (/kernel/misc/rsmops).
-
Header files providing API function and data structure prototypes (/opt/SUNWrsmdk/include).
-
An optional extension to librsm.so that provides RSM support for the specific interconnect that is configured in the system. The extension is provided in the form of a library (librsminterconnect.so).
API Library Functions
The API library functions support the following operations:
Interconnect controller operations
Cluster topology operations
Memory segment operations including segment management and data access
Barrier operations
Event operations
Interconnect Controller Operations
The controller operations provide mechanisms for obtaining access to a controller and determining the characteristics of the underlying interconnect. The operations include:
Get controller
Get controller attributes
Release controller
rsm_get_controller
int rsm_get_controller(char *name, rsmapi_controller_handle_t *controller);
The rsm_get_controller operation acquires a controller handle for the given controller instance (for example, sci0 or loopback). The returned controller handle is used for subsequent RSM library calls.
Return Values: Returns 0 if successful; returns an error value otherwise.
| RSMERR_BAD_CTLR_HNDL | Invalid controller handle |
| RSMERR_CTLR_NOT_PRESENT | Controller not present |
| RSMERR_INSUFFICIENT_MEM | Insufficient memory |
| RSMERR_BAD_LIBRARY_VERSION | Invalid library version |
| RSMERR_BAD_ADDR | Bad address |