Maintaining Application Information
Applications that want to receive ToolTalk messages provide information to the ToolTalk service that describes what kind of messages they want to receive. This information, known as message patterns, is provided dynamically either by applications as they run, or through ptype and otype files.
Installing Application Types
Installing application types is an occasional task; you only need to install type information when new types are created, or when an application error condition exists. Ptype and otype files are run through the ToolTalk type compiler at installation time. tt_type_comp merges the information into the ToolTalk Types Database. The application then tells the ToolTalk service to read the type information in the database.
To install an application's ptype and otype files, follow these steps:
Run tt_type_comp on your type file.
% tt_type_comp your-file
tt_type_comp runs your-file through cpp, compiles the type definitions, and merges the information into a ToolTalk Types table. Table 5-1 describes location of the XDR-base format tables; Table 5-2 describes the location of the Classing Engine-base format table.
Note - The Classing Engine interface exists for compatibility reasons only. The default is XDR.
Table 5-1 XDR-base Format ToolTalk Types Tables
Database
Uses XDR Table
user
~/.tt/types.xdr
system
/etc/tt/types.xdr
desktop
/usr/dt/appconfig/tttypes/types.xdr
network
$OPENWINHOME/etc/tt/types.xdr
Table 5-2 Classing Engine-base Format ToolTalk Types Tables
Database
Uses Classing Engine Table
user
~/.cetables/cetables
system
/etc/cetables/cetables
network
$OPENWINHOME/lib/cetables/cetables
There are four XDR databases. The $TTPATH environment variable determines which three will be used. See tt_type_comp(1) for details about the format and priority of $TTPATH entries.
By default, tt_type_comp uses the user database. To specify another database, use the -d option. For example:
% tt_type_comp -d user|system|[network|desktop]your_file
Note - When you run tt_type_comp on your ptype or otype files, it first runs cpp on the file and then checks the syntax before it places the data into the ToolTalk Types Database format. If syntax errors are found, a message is displayed that indicates the line number of the cpp file. To find the line, enter: cpp -P source-file temp-file and view the temp-file to find the error on the line reported by tt_type_comp.
ttsession will reread the ToolTalk Types Database automatically.
To force ttsession to reread the ToolTalk Types Database, see the "Updating the ToolTalk Service".
Examining ToolTalk Type Information
You can examine all type information in a specified ToolTalk Types Database, only the ptype information, or only the otype information. To specify the database you want to examine, use the -d option and supply the name of the user, system, or network to indicate the desired database. If the -d option is not used, tt_type_comp will use the user database by default.
To examine all the ToolTalk type information in a ToolTalk Types Database, enter the following line
% tt_type_comp -d user|system|network -p
The type information will be printed out in source format.
To list all ptypes in a ToolTalk Types Database, enter the following line:
% tt_type_comp -d user|system|network -P
The names of the ptypes will be printed out in source format.
To list all otypes in a ToolTalk Types Database, enter the following line:
% tt_type_comp -d user|system|network -O
The names of the otypes will be printed out in source format.
Removing ToolTalk Type Information
You can remove both ptype and otype information from the ToolTalk Types Databases.
% tt_type_comp -d user|system|network -r type |
For example, to remove a ptype called EditDemo from the ToolTalk Types network database of a sample application, enter the line:
% tt_type_comp -d network -r EditDemo |
After you remove type information, force any running ttsessions to reread the ToolTalk Types Database again to bring the ToolTalk service up-to-date. See "Updating the ToolTalk Service" for more information.
Updating the ToolTalk Service
When you make changes to the ToolTalk Types Database with tt_type_comp(1), the ToolTalk Service will automatically be notified to reread the types files. If you wish to explicitly force a ToolTalk session that is already running to reread the databases, send the ttsession process a SIGUSR2.
 To send the ttsession process a SIGUSR2:
To send the ttsession process a SIGUSR2:
Enter the ps command to find the process identifier (pid) of the ttsession process
% ps -ef | grep ttsession
Enter the kill command to send a SIGUSR2 signal to ttsession.
% kill -USR2 ttsession_pid
Process Type Errors
One or both of the following conditions exists if applications report the error:
Application is not an installed ptype. |
The ToolTalk service has not been instructed by the application to reread the recently updated type information in the ToolTalk Types Database. See "Updating the ToolTalk Service" for instructions on how to force the ToolTalk service to reread type information from the ToolTalk Types Database.
The application's ptypes and otypes have not been compiled and merged into the ToolTalk Types Database. See "Installing Application Types" for instructions on how to compile and merge type information.
Using ttsnoop to Debug Messages and Patterns
ttsnoop is a tool provided to create and send custom-constructed ToolTalk messages. You can also use ttsnoop as a tool to selectively monitor any or all ToolTalk messages. The ttsnoop program resides in the directory /usr/dt/bin/ttsnoop. To start the program, enter the following command on the command line:
% /usr/dt/bin/ttsnoop [ -t ] |
The -t option displays the ToolTalk API calls that are being used to construct a particular pattern or message. Figure 5-1 shows the window that is displayed when ttsnoop starts.
Figure 5-1 ttsnoop Display Window
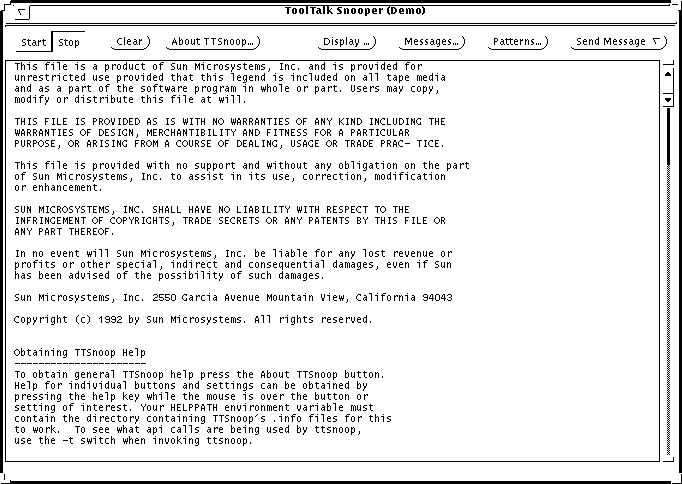
Start
Press this button to activate message reception. ttsnoop will display any incoming messages which match the patterns you register.
About TTSnoop
Press this button to obtain general help for ttsnoop.
Note - To obtain help for individual buttons and settings, place the mouse over the button or setting and press the F1 key or Help key on your keyboard. Your HELPPATH environment variable must contain the directory that contains the TTSnoop .info files.
Display
Press this button to popup a panel of checkboxes to highlight specific ToolTalk message components on the ttsnoop display subwindow.
Messages
Press this button to popup a panel which enables you to create, store, and send ToolTalk messages.
Patterns
Press this button to popup a panel which allows you to compose and register ToolTalk patterns.