To Configure the System Containing the Action Definition
To Configure the System Containing the Action Definition
Provide the operating system network configurations required by the desktop.
See "Configuring Base Operating System Networking for the Desktop".
Provide the general desktop configuration required for servers.
Create and install the action definitions and application groups.
See "Creating Actions that Run Applications on Remote Systems" and "Creating and Administering General Application Groups".
 To Configure the Session Server
To Configure the Session Server
Provide the operating system network configurations required by the desktop.
See "Configuring Base Operating System Networking for the Desktop".
Provide the general desktop configuration required for clients.
Modify the actions search path to include the database host.
Modify the application search path to include the execution host.
Running Applications Locally
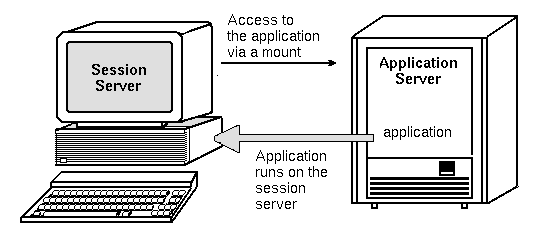
The standard application server configuration runs applications on the application server. Sometimes it is desirable to have the application installed on a remote system but executed locally on the session server.
Figure 7-6 Execution across mount points
 To Configure the Application Server
To Configure the Application Server
No special configuration is required.
 To Configure the Session Server
To Configure the Session Server
For example, you might use the following variable definition to find an application registered on sysAAA:
DTSPSYSAPPHOSTS=/net/SysAAA/etc/dt/appconfig/appmanager/C |
The session server must be able to access the application's configuration files, such as app-defaults, message catalogs, and shared libraries.