| C H A P T E R 3 |
Domain Administration |
The SSP supports commands that let you logically group system boards into Dynamic System Domains, or simply domains , which are able to run their own operating system and handle their own workloads. Domains can be created and deleted without interrupting the operation of other domains. You can use domains for many purposes. For example, you can test a new operating system version or set up a development and testing environment in a domain. In this way, if problems occur, the rest of your system is not affected.
You can also configure several domains to support different departments, with one domain per department. You can temporarily reconfigure the system into one domain to run a large job over the weekend.
You can create a domain out of any group of system boards, provided the following conditions are met:
The boards are present and not in use in another domain.
At least one board has a network interface.
The boards have sufficient memory to support an autonomous domain.
The name you give the new domain is unique (as specified in the domain_create (1M) command) and this name matches the host name of the domain to be booted (as specified by the SUNW_HOSTNAME environment variable).
You have an eeprom.image file for the domain that was shipped to you by the factory. If your eeprom.image file has been accidentally deleted or corrupted and you do not have a backup, see To Recreate the eeprom.image File .
There must be at least one boot disk connected to one of the boards that will be grouped together into a domain. Alternatively, if a domain does not have its own disk, there must be at least one network interface so that you can boot the domain from the network.
|
Note - Before proceeding, read the requirements in the previous section, Domain Configuration Requirements. If the system configuration must be changed to meet any of these requirements, call your service provider. Also, after you create a domain, you must update /etc/hosts to reflect the new name of the domain. |
1. Click the left mouse button on the first board.
2. Click the middle mouse button on any additional boards.
Ensure that the boards you select do not currently belong to any domain.
3. Choose Domain then Create from the Configuration menu.
The Create Domain window is displayed ( FIGURE 3-1 ).
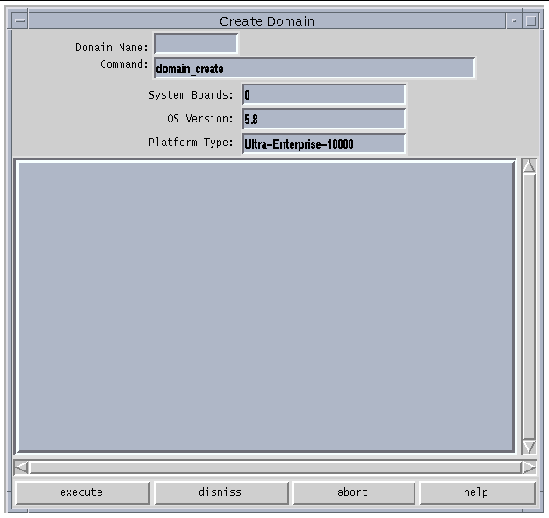
The name of the domain must be the one given to you by the factory and contained in the eeprom.image file. It cannot be an arbitrary name.
6. If all other fields are acceptable, click execute.
Note that the System Boards field indicates the boards that you selected in the main Hostview window. The default OS version and the default platform type are shown.
If Hostview successfully executes the command, it displays the message Command completed in the informational panel of the window.
|
Note - Hostview can run only one create or remove command at a time. If you attempt to execute a second create or remove command before the first has completed, your second attempt fails. |
|
Note - Before proceeding, see Domain Configuration Requirements. If the system configuration must be changed to meet any of these requirements, contact your service provider. |
domain_name is the name you want to give to the new domain. It should be unique among all Sun Enterprise 10000 systems controlled by the SSP.
system_board_list specifies the boards that are to be part of this domain. The specified system boards must be present and not in use. Each domain must have a network interface, disk interface, and sufficient memory to support an autonomous system. List the board numbers, separated by commas or spaces, for all boards you want to include.
os_version is the version of the operating system to be loaded into the domain.
platform_name is the name of the platform managed by the SSP.
2. Optionally, create a new SSP window for the domain, as described in SSP 3.5 Window .
Use the domain_switch (1M) command to set the SUNW_HOSTNAME environment variable to the new domain name.
1. Log in to the SSP as user ssp .
2.
Recreate the
eeprom.image
file.
|
Note Note - All key and host_id numbers are case sensitive and must be entered exactly as they are received. |
a. For the first domain, type:
domain_name is the hostname of the domain
serial_number is the number provided with the key in the form of 0XA65 xxx
b. For all subsequent domains, type:
domain_name is the hostname of the domain.
hostid is the number provided with the key in the form of 0X80A66 xxx .
3. Check the result by typing:
In the following example, 49933C54C64C858CD4CF is the key and 0x80a66e05 is the host_id
4. Back up the SSP eeprom.image files to tape or disk where they can be accessed in case of SSP boot disk failure.
1. In the main Hostview window, click any board in the domain to be removed.
2. Choose Domain then Remove from the Configuration menu.
The Remove Domain window is displayed ( FIGURE 3-2 ).
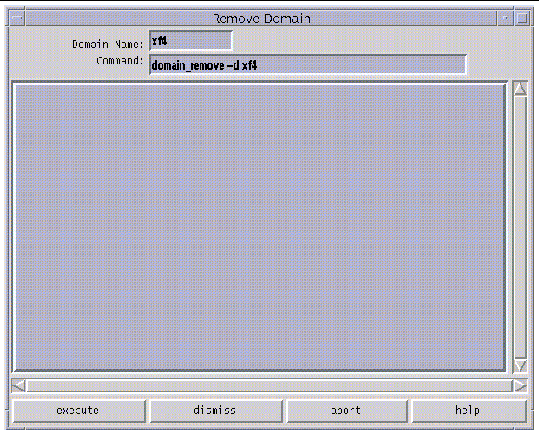
3. If the default domain_remove (1M) command is satisfactory, click the execute button; otherwise, edit the command first.
For help on the domain_remove (1M) command, click the help button. A help window is displayed (see Help Window ).
4. Specify whether or not domain subdirectories should be removed when you are prompted to do so.
The pathnames of the subdirectories are displayed. These subdirectories contain domain-specific information such as message files, configuration files, and hpost (1M) dump files. You can keep these directories if you still need the information. It is easier to recreate a domain if you keep these directories.
|
Note Note - If the system cannot remove your domain, see domain_remove(1M) for a list of potential errors. |
The domain must not be running the operating system.
2. Specify whether or not domain subdirectories should be removed when you are prompted to do so.
The pathnames of the subdirectories are displayed. These subdirectories contain domain-specific information such as message files, configuration files, and hpost (1M) dump files. You can keep these directories if you still need the information. The domain can be recreated whether or not you keep this information.
3. Type
domain_status
(1M) to verify that the domain was removed.
|
Note Note - If the system cannot remove your domain, an error message is displayed. See domain_remove(1M) for a list of potential errors. |
1. Use the mouse to select any system board belonging to the domain you want to bring up.
2. Choose Bringup from the Control menu.
A window is displayed that shows the name of the selected domain.
3. Click Execute to perform the bringup.
4. After the bringup operation has completed, choose netcontool from the Terminal menu.
5. Click the Connect button to open a netcon (1M) window.
6. If the OBP prompt appears (that is, the OK prompt), boot the domain:
The domain should boot and then display the login prompt. Note that you can use the OBP command devalias to determine the alias for the disk you want to use as boot_device .
Before you can bring up a domain from the command line in an SSP window, the system boards for the domain must be powered on. Ensure that the SUNW_HOSTNAME environment variable is set to the proper valid domain name.
1. As user ssp , set the SUNW_HOSTNAME environment variable by typing:
where domain_name is the name of the domain you want to bring up.
2. Power on the power supplies for all of the boards in the domain:
3. Bring up the domain by typing:
The -A option is the autoboot option. If the autoboot option is on, the domain will automatically boot. If it is off, you need to explicitly boot the domain from the OBP prompt. For information on other command line options, see the bringup (1m) man page.
 Choose Domain then Status from the Configuration menu.
Choose Domain then Status from the Configuration menu.
The Domain Status window is displayed ( FIGURE 3-3 ).
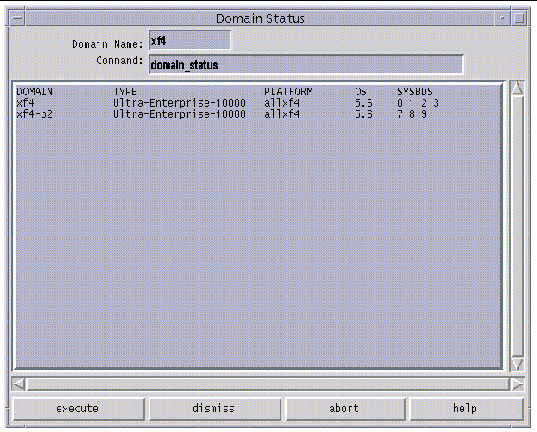
The status listing is displayed in the main panel of the window. The following table explains the columns in the Domain Status window.
|
Note Note - You can determine which DR model is running on your domains by entering the -m option after the domain_status command in the Command box, then clicking the execute button. The information displayed will include the DR model, which is either 2.0, 3.0, or unknown, as explained in TABLE 3-1. |
1. Log in to the domain as superuser and run the shutdown (1M) command.
A message indicates that the system has been halted.
1. Log in to the domain as superuser.
2. Run sys-unconfig (1M) to deconfigure the host.
3. Back up the
eeprom.image
files in the directory
/var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private/eeprom_save
.
4. Change the host name in the NIS and the /etc/hosts files on the SSP to reflect the name of the new domain.
5. As user ssp , in the main Hostview window, select a board from the domain that you want to rename by clicking on it with the left mouse button.
6. Choose Domain then Rename from the Configuration menu.
The Rename Domain window is displayed ( FIGURE 3-4 ).
7. If the default domain_rename (1M) command is satisfactory, click the execute button. Otherwise, edit the command first.
For help on the domain_rename (1M) command, click the help button. A help window is displayed (see Help Window ).
8. Bring up the domain using Hostview or the bringup (1M) command.
For details, see To Bring up a Domain From Within Hostview and To Bring up a Domain From the Command Line .
9. Start a netcon (1M) session and answer the prompts regarding the configuration of the domain.
1. Log in to the domain as superuser.
2. Run sys-unconfig(1M) to deconfigure the host.
3. Back up the
eeprom.image
files in the directory
/var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private/eeprom_save
.
4. Change the host name in the NIS and the /etc/hosts files on the SSP to reflect the name of the new domain.
5. As user ssp , rename the domain.
For more information, see the domain_rename (1M) man page.
6. Bring up the domain using Hostview or the bringup (1M) command.
For details, see To Bring up a Domain From Within Hostview and To Bring up a Domain From the Command Line .
7. Start a netcon (1M) session and answer the prompts regarding the configuration of the domain.
|
|
1. Log in to the domain as user ssp .
2. Change the SunOS operating system version for the domain by using the domain_rename command.
domain_name is the name of the domain to be changed
new_os_version is the version of the SunOS operating systems, for example, 5.5.1, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, or 5.9, to be run on the domain.
Copyright © 2002, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.