Configuring DHCP Service (Task)
When you configure DHCP service on your network, you configure and start the first DHCP server. Other servers can be added later, and may access the same data from a shared location if the data store supports shared data. This chapter includes procedures to enable you to configure the DHCP server and place networks and their associated IP addresses under DHCP management. It also explains how to unconfigure a server.
This chapter also provides instructions for procedures that use both DHCP Manager and the dhcpconfig utility in separate sections. This chapter contains the following information:
"Configuring and Unconfiguring a DHCP Server Using DHCP Manager"
"Configuring and Unconfiguring a DHCP Server Using dhcpconfig Commands"
Configuring and Unconfiguring a DHCP Server Using DHCP Manager
This section includes procedures to help you configure and unconfigure a DHCP server with DHCP Manager. Note that you must be running an X Window system such as CDE to use DHCP Manager.
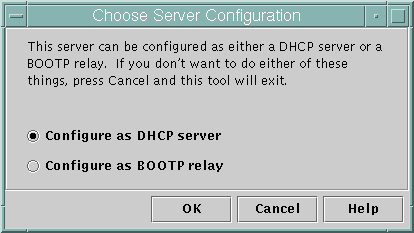
When you run DHCP Manager on a server not configured for DHCP, the following screen is displayed to allow you to specify whether you want to configure a DHCP server or a BOOTP relay agent.
Figure 9-1 Choose Server Configuration Dialog Box
Configuring DHCP Servers
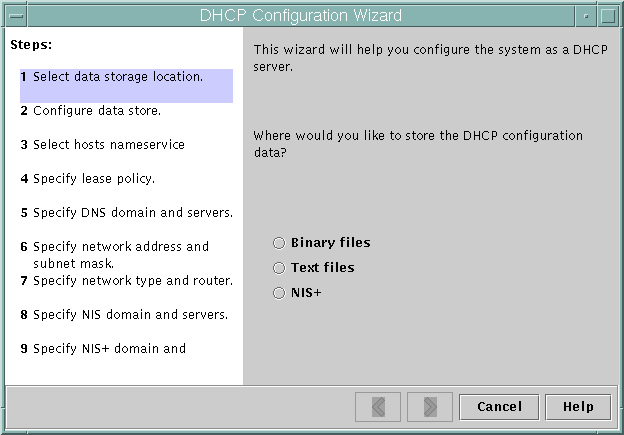
When you configure a DHCP server, DHCP Manager starts the DHCP Configuration Wizard, which prompts you for information needed to configure the server. The initial screen of the wizard is shown in the following figure.
Figure 9-2 DHCP Configuration Wizard's Initial Screen
When you finish answering the wizard prompts, DHCP Manager creates the items listed in the following table.
Table 9-1 Items Created During DHCP Server Configuration
 How to Configure a DHCP Server (DHCP Manager)
How to Configure a DHCP Server (DHCP Manager)
Select the system you want to use as a DHCP server.
Use the guidelines in "Making Decisions for DHCP Server Configuration (Task Map)".
Make decisions about your data store, lease policy, and router information.
Use the guidelines in "Making Decisions for DHCP Server Configuration (Task Map)".
Become superuser on the server system.
Type the following command:
#/usr/sadm/admin/bin/dhcpmgr &
Choose the option Configure as DHCP Server.
This starts the DHCP Configuration Wizard, which helps you configure your server.
Select options or type requested information based on the decisions you made in the planning phase.
If you have difficulty, click Help in the wizard window to open your web browser and display help for the DHCP Configuration Wizard.
Click Finish to complete the server configuration when you have finished entering the requested information.
At the Start Address Wizard window, click Yes to configure addresses for the server.
The Address Wizard enables you to specify which addresses to place under the control of DHCP.
Answer the prompts based on decisions made in the planning phase.
See "Making Decisions for IP Address Management (Task Map)" for more information. If you have difficulty, click Help in the wizard window to open your web browser and display help for the Add Addresses Wizard.
Review your selections, and click Finish to add the addresses to the network table.
The network table is updated with records for each address in the range you specified.
You can add more networks to the DHCP server with the Network Wizard, as explained in "Adding DHCP Networks".
Configuring BOOTP Relay Agents
When you configure a BOOTP relay agent, DHCP Manager takes the following actions:
Prompts you for IP addresses of the DHCP server to which requests should be relayed.
Edits /etc/inet/dhcpsvc.conf, to specify the options needed for BOOTP relay service.
The following figure shows the screen displayed when you choose to configure a BOOTP relay agent.
Figure 9-3 Configure BOOTP Relay Dialog Box
 How to Configure a BOOTP Relay Agent (DHCP Manager)
How to Configure a BOOTP Relay Agent (DHCP Manager)
Select the system you want to use as a BOOTP relay agent.
Become superuser on the server system.
Type the following command:
#/usr/sadm/admin/bin/dhcpmgr &
If the system has not been configured as a DHCP server or BOOTP relay agent, the DHCP Configuration Wizard starts. If the system has already been configured as a DHCP server, you cannot configure it as a BOOTP relay agent unless you unconfigure the server first. See "Unconfiguring DHCP Servers and BOOTP Relay Agents".
Select Configure as BOOTP Relay.
The Configure BOOTP Relay dialog box opens.
Type the IP address or host name of one or more DHCP servers that are configured to handle BOOTP or DHCP requests received by this BOOTP relay agent, and click Add.
Click OK to exit the dialog box.
Notice that the DHCP Manager offers only the File menu to exit the application and the Service menu to manage the server. Other menu options are disabled because they are useful only on a DHCP server.